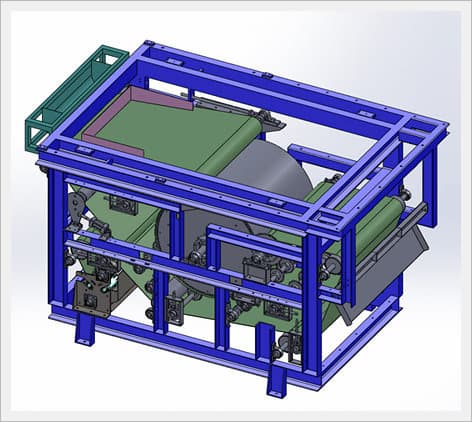
Electric Dehydrator
Negotiable Min Order Quantity Unit
- Required Quantity
-
- Place of Origin
- Payment Terms
- Negotiable
- Production method
- Negotiable
- Shipping / Lead Time
- Negotiable / Negotiable
- Keyword
- Category
- Other General Industrial Equipment
E&D Global
- Country / Year Established
-
 South Korea
/
South Korea
/
- Business type
- Others
- Verified Certificate
-
12

| Product name | Electric Dehydrator | Certification | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Other General Industrial Equipment | Ingredients | - |
| Keyword | - | Unit Size | - |
| Brand name | - | Unit Weigh | - |
| origin | Stock | - | |
| Supply type | - | HS code | - |
Product Information
Electric Dehydrator Technology Introduction
* Abstract of sludge dewatering technology
Sludge dewatering method is intended to eliminate water from sludge, to enhance operating cost reduction effect and resource values, as well as to reduce transportation cost up to the final disposal and to cause no trouble for land disposal techniques.
* Classification of sludge dewatering technology
a. Filtering dehydration method
01 Method by the drying bed
A method of infiltration drainage into the filter bed and drying on the surface after allowing the sludge flow on to the filter bed where sand or filtering materials have been laid
02 Drying Lagoon
A drying method to put sludge in the lagoon for precipitation, to send supernatant back to the disposal facility, and evaporate the sludge of 0.7~1.4m depth
b. Mechanical dewatering method
01 Vacuum dehydrator (Vacuum Filter)
- A dewatering method where the outer circumference of spin drum is covered by filtering cloth, negative pressure(300~600mmHg) in the drum inside is maintained by a vacuum pump, and the drum rotates.
02 Pressing dehydrator (Filter press)
- A dewatering method to pressurize the sludge wrapped by filtering cloth
03 Centrifugal dehydrator (Screw decanter)
- A dewatering method by gravity after receiving centrifugal effect of 1,000~3,000G resulting from rotating movement of solid particles
04 Belt press
- A method to dewater the sludge continuously by one or two moving belt.
- A dewatering method by gravity when the sludge reformed by organic polymer coagulant is injected into the belt press, and by pressure between rollers along the movement of belt.
05 Screw press
- A dewatering method by compressing and extruding the condensed sludge with screw
C. Analysis by the kinds of dehydrators
|
Item
|
Our technology
|
Existing technology
|
|||
|
Dewatering
type |
Electric
Dewatering |
Filter
press |
Screw
decanter |
Belt
press |
Vacuum
filter |
|
Picture
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Applied
principle |
Electric infiltration
|
Sludge supply pressure
|
Centrifugal force
|
Filter cloth
|
Decompression filtering
|
|
Applied
agent |
Not applicable
|
Polymer coagulant
|
Polymer coagulant
|
Polymer coagulant
|
Polymer coagulant
|
|
%of water
content after dewatering |
below 65wt%
|
80~70wt%
|
80~70wt%
|
80~70wt%
|
80~70wt%
|
|
Operating
cost |
Electricity cost
|
Added electricity cost of high pressure dewatering part
|
Less power consumption ratio
|
Added electricity cost of high pressure dewatering part
|
big energy consumption
|
|
Service
pressure |
Simple compression except for power supply
|
15kg/cm2
|
1500~3000G
|
10~20kg/m3/hr
|
10~25kg/m3/hr
|
|
Incidental
facilities |
Steam removal facility
|
Reaction facility
Drug facility Cleaning facility |
Cleaning facility
Soundproof facility Dedusting facility |
Reaction facility
Drug facility |
Agitating device in Vat
Cleaning device Dewatered cake discharge conveyor |
|
Sludge
supply method |
Continuous
|
Intermittent
|
Continuous
|
Continuous
|
Continuous
|
|
Applicability
against sludge behavior change |
Good
|
Good
|
Bad
|
Good
|
Ordinary
|
|
Others
|
Disposal efficiency varies with the quantity of power supply
|
Continuous work is difficult due to Batch type operation
|
Solid recovery is small.
Issue of high rotation |
Drug injection is required.
|
Intoxication
Many incidental facilities |
Principles and advantage of electric dewatering technology
Definition of Sludge
Sludge is called Oh-Nee in Chinese language.
Sludge in the dictionary means a solid substance settled down from the floating matters when sewage is precipitated in water tank or reservoir.
Diverse sludges are obtained during several stages of sewage treatment process. That is, at the first stage chemically settled sludge is obtained, then sludge activated by a drip filter is obtained, and retted sludge is obtained. Some sludge is sent to the ocean after treated with the underwater dumping method or water pumping method, some is sold as a fertilizer after being dried, and some is retted after anaerobic treatment in the water reserver like an imhoff tank or precipitation tank with microbes to reduce organic components. During the retting process, as its volume decreases, and residues are comparatively harmless, characterized of humus soil, it is filled in the land. When we see the definition of "Wastes" in Article 2, Waste Management Law, they are garbages, burnt matters, Oh-Nee, waste oil, waste acid, waste alkaline, animal corpses, and substances not required further for human life or business activity. Oh-Nee is included here in the category of waste, but the definition is not stated as a separate title and dispersed in several titles.
To explain more easily, a mixture of solid foreign materials(microbes, etc.) input or created during the purification process of fine solids (dust, etc.) mixed in sewage and waste water - 98% of water content concentrated or condensed during the purification process - is called slurry. First-dewatered slurry, 80% of water content, is called cake sludge.
Sludge production details
Sewage and wastewater include fine solids (dust, etc.) mixed during the use of water and microbic solid foreign materials input or created during the purification process. At the final stage of sewage and wastewater purification process, used is a method to separate from water the foreign materials by condensing them only normally with the input of chemicals of polymer
This condensed state is called 'Slurry'. a limp shape of 98% of water content in general (98% water, 2% solids)
This slurry is discharged separately and goes through dewatering process. Most dehydrating equipment currently installed at the sewage and wastewater treatment plant are 'belt press dewaterers' or centrifugal separation dewaterers'. A lump of final foreign materials through such dehydration process is called 'Sludge', which is normally 80% of water content (80% water, 20% solids) characteristic of watering out when holding it in the hand and pressing it.
Currently the technology of dehydration below 80% in average of water content in sludge does not exist all over the world. The reason is that we cannot draw internal water in the microbic cytoplasm, a major constituent of sludge.
Technical principle of the electric dehydrator
- To utilize "electroosmosis", one of electric inherent properties, and to utilize incidentally electro-phoresis", and "Brown motion".
- To utilize the power supply method using voltage difference, to break sludge cell membranes, and thus to discharge water in the cell

Sludge cell breaking process by electric dehydration

slurry to 70%. We contribute to sludge fuel energy business by further evolving the technology which reduces 80% cake first dehydrated to 60%.
At present our technology is introduced to domestic sewage and wastewater treatment plant and private companies for cost reduction and corporate image enhancement for improving environment. Our company is leaping toward a global environment enterprise through interchange, collaboration, and export with companies in Europe, China, USA, and Asian countries.
We are performing a leading role in true-to-the-name electric dewatering technology by securing stability, efficiency, and technique of electric dehydrators, after overcoming previous problems by rich site application experiences

Sludge treatment process of the electric dehydrator

Product specification of the electric dehydrator
|
Item
|
Contents
|
|
|
Kind of product
|
Complex type electric dehydrator
(EDG-C2400) |
Standard type electric dehydrator
(EDG-S2400) |
|
Product
picture |
 |
 |
|
Dewatered
object |
slurry(over 98% of water content)
|
sludge cake(around 80% of water content)
|
|
%of water content
after dehydration |
65~70%
|
60±3%
|
|
Optional
specification |
Replacement for the existing dehydrator
Replacement for the new dehydrator |
Secondary dehydration at the rear part of the existing dehydrator
|
|
Belt width
(mm) |
2,460
|
2,460
|
|
Treated
amount (ton/hr) |
8~10ton
(based on 98~98% slurry) |
1ton
(based on 80% sludge cake) |
|
Power
consumption (kwh) |
150
|
150
|
|
Size
(LxWxH) |
3510x3424x3430
|
3354x3510x3204
|
|
Scope of
supply |
Console, VAR system
|
Console, VAR system
|
|
Input principle
|
Transport slurry and coagulant through pipe with a motor, agitate in the agitator, put the slurry into the input device with a slurry head (windmill type) | Put into the sludge supply device, the sludge discharged from the first dehydrator and stored in the hopper, and supply it to the dehydrator in the fixed quantity in accordance with the sludge characteristics. |
Drawing of the electric dehydrator
a. Drawing of complex type electric dehydrator(EDG-C2400)

b. Drawing of standard type electric dehydrator(EDG-S2400)

List of required power
|
Item
|
Model
|
Specification
|
Q'ty
|
Required
power(kw) |
Manufacture
|
|
Required
power |
Complex type electric dehydrator
|
150Kw/3Ø/380V
|
1
|
146
|
E&D
Global |
|
Standard type electric dehydrator
|
150Kw/3Ø/380V
|
1
|
146
|
||
|
Ordinary
power required |
Main driver
|
1.5Kw/3Ø/220/380V
|
1
|
1.5
|
Samyang
Reduction Gear |
|
Drum cleanser
|
0.4Kw/3Ø/220/380V
|
1
|
0.4
|
||
|
Filter cloth cleaner
|
0.4Kw/3Ø/220/380V
|
1
|
0.4
|
||
|
Supply of fixed amount of sludge
|
0.4Kw/3Ø/220/380V
|
1
|
1.2
|
||
|
Console
|
0.4Kw/3Ø/220/380V
|
1
|
0.4
|
Vendor
|
|
|
Others
|
-
|
0.1
|
-
|
||
|
Total
|
150
|
Consumable details
|
No.
|
Product Name
|
Q'ty
|
Material
|
Time
|
|
1
|
Drum
|
1set
|
Titanium
|
7,500
|
|
2
|
Filter cloth
|
1set
|
DM-101
|
4,000
|
|
3
|
Discharge scraper
|
1set
|
MC NYLOM
|
4,000
|
|
4
|
Drum brush
|
1set
|
PP
|
4,000
|
|
5
|
Filter cloth belt brush
|
1set
|
PP
|
4,000
|
|
6
|
Surge belt of the fixed quantity supply device
|
1set
|
PVC
|
5,000
|
|
7
|
Power supply device(brush)
|
1set
|
Carbone(>80%)
|
8,000
|
|
8
|
Mechanical valve
|
1set
|
PMSV2406-VA-02
|
4,000
|
|
9
|
Electric valve
|
1set
|
Electric type/Screw type
|
4,000
|
|
10
|
Limit switch
|
1set
|
AC220V
|
1,000
|
|
11
|
Fixed quantiy supply leveller
|
1set
|
HILV-100
|
4,000
|
|
12
|
Bearing
|
1set
|
UV bearing
|
2,500
|
|
13
|
Cylinder
|
1set
|
GDC80-100
|
1,000km
|
* This period table may be changed according to the site conditions and user's management.
* Replacement is requested after checking the state of consumables.
Maintenance cost calculation and details
Design criteria of hydrator [Operating condition of the standard type hydrator: 8 hours]
[Design capacity based on 8~10ton/day] [based on 80% of water content]
|
Item
|
Design
capacity |
Input %of
water content |
%of water
content in discharge |
Operating
hour |
Treated
quantity |
|
Sludge cake
|
8~10ton/day
|
80%
|
60±3%
|
8~10hr
|
0.8~1ton
|
Design criteria → Operating hour for one dehydrator is 8~10hr
For the operation of 8~10 hours/day, one dehydrator should be installed.
Maintenance cost
Calculation conditions
01 Electricity cost
[Power consumption calculation]
|
Construction
type |
Equipment
name |
Power
(kw) |
Quantity(set)
|
Service
operation hour(hr) |
Applied load
(kw.h.day) |
|
|
Service
|
Total
|
|||||
|
Sludge
dewatering facility |
Electric
dehydrator |
150
|
1
|
1
|
8
|
1,200
|
* Calculation basis of electricity cost
ㆍ Operating condition - dehydrator 1 set (8~10hr/day)
ㆍ Design specification - Power consumption 150kw/set
ㆍ Charge
- Basic rate 150kw x 1(set) x W6,970 = W1,045,500
- Electricity rate used 150kw x 1(set) x 8(hr/day) x W77.18= W92,616
* 2010. 08. 01. Increase of electricity rate (about 17% increase compared with that in 2008)
* Basic rate W6,970/Kw(Monthly)
* Unit rate W77.18/Kwh(average per season) Unit rate in 2008 W62.55/Kwh
* Unit rate reduced by 16% for 24 hours operation (reduction in case of night use)
02 Water capacity
|
Construction
type |
Equipment
name |
Used
amount (m3) |
Quantity(set)
|
Service
operation hour(hr) |
Applied
quanity (m3/day) |
|
|
Service
|
Total
|
|||||
|
Sludge
dewatering facility |
Standard type electric dehydrator
(EDG-S2400) |
1
|
1
|
1
|
8
|
8
|
* Calculation basis of water capacity - Used amount(m3) x 1(set) x 8(operating hour per day) = 8m3/day
03 Consumables and repair/maintenance costs
* Consumable costs : calculation of consumable costs
- Main consumables: Drum re-coating costs of the electric dehydrating device (W25mil./year/set)
→ Drum re-coating cost = W25,000,000/year
* Repair cost : Replacements of tools and material like filters, replaced quantity, and relevant costs
- General consumable costs : 0.5% of mechanical device costs:W2,500,000/year
Calculation details of operation cost per ton
|
Item
|
Unit price
applied |
Amount per
day |
Yearly
consumption cost |
Remarks
|
|
|
Electricity
cost |
Contract power (150Kw)
|
W6,970/kw
|
1,045,500
|
12,546,000
|
|
|
Electricity used
|
77.18/kwh
|
92,616
|
30,563,280
|
||
|
Total
|
43,109,280
|
||||
|
Water cost
|
Used water
|
W917/m3
|
8
|
2,420,880
|
|
|
Fuel cost
|
Not applicable
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
Consumable cost
|
Drum re-coating cost
|
25,000,000
|
8,800,000
|
Yearly 1set
(Replacement period: 7500 hrs) |
|
|
Repair/
maintenance cost |
0.5% of mechanical
equipment cost |
2,500,000
|
2,500,000
|
||
|
Labor cost
|
Operator
|
24,000,000
|
48,000,000
|
2 persons
|
|
|
Total
|
104,830,160
|
||||
|
Operating cost per ton
(80% → 60% of water content) |
W39,708/ton
|
||||
*Excluding civil work and other utility costs
Economy of the electric dehydrator
Our dewatering technology uses electroosmosis and electrophoresis instead of physical force, allowing up to 60% of water content as it destruct sludge particles with electric action and dehydrate internal water. As dewatered sludge loses its intrinsic property and non-dry section, the following dry method can be simple and the cost will greatly be reduced for advantage. Besides, compared with existing technologies, its facility and operating costs can be reduced down to 1/2. It, as a realistic and core technology, can also be applied to pre-treatment technology to any sludge land treatment techniques
Comparison of economic feasibility for the electric dehydrator (10 ton, 80% sludge cake per day)
|
Item
|
Unit
|
Comparison before/after dehydration
|
|||
|
Before
hydration (82%) |
After
dehydration (60%) |
After
dehydration (50%) |
|||
|
Sludge production
|
ton/day
|
10
|
4.5
|
3.6
|
|
|
Water reduction rate
|
%/day
|
-
|
55.0
|
64.0
|
|
|
Power consumption
|
kwh/ton
|
130
|
135
|
||
|
Electric cost
|
Unit
cost |
W/Kwh
|
80
|
80
|
|
|
Calculation
|
W/day
|
104,000
|
108,000
|
||
|
Sludge
transportation cost |
Unit
cost |
W/ton
|
20,000
|
20,000
|
20,000
|
|
Calculation
|
W/day
|
200,000
|
90,000
|
72,000
|
|
|
Sludge
disposal cost |
Unit
cost |
W/ton
|
60,000
|
60,000
|
60,000
|
|
Calculation
|
W/day
|
600,000
|
270,000
|
216,000
|
|
Economic feasibility analysis of electric dehydrator and dry system(10ton/day, 82→60% dry)
|
Item
|
Electric dehydrator
|
Dryer system
|
|
|
In case of useing LNG
W900/m3 |
In case of using kerosene
W1,500/L |
||
|
Yearly
energy cost |
150Kwh x 10ton x 365day x W80/Kwh
=W43,800,000 |
45m3 x 10ton x 365day x W900/m3
=W147,825,000 |
55L x 10ton x 365day x W1,500/L
=W301,125,000 |
B2B Trade
| Price (FOB) | Negotiable | transportation | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Negotiable | Leadtime | Negotiable |
| Payment Options | Negotiable | Shipping time | Negotiable |
- President
- Kwangsun Park
- Address
- 5F Shinhan building, 1294-18 Chipyeong-dong, Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
- Product Category
- Waste Management
- No. of Total Employees
- 1-50
- Company introduction
-
E&D Global was founded in 2012 as a global environmental company under the banner of green growth, the fundamental topic for human life. We have developed and completed new technologies for sludge reduction and succeeded in commercialization through our endless technical development and intense field experiences. Everyday we dump more than 10,000ton of sludge at sea, which causes marine environment pollutions that is on the rise as a serious problem at government level. Therefore, the government has prohibited a dumping of sludge at sea since 2012 and each of the local governments are considering alternatives for overland disposal of sludge. E&D Global has succeeded in solving all of these problems by a long technical development and great expense. 'Electro-osmosis Dehydrating' and 'Low-temperature Ventilation and Drying', both technologies completed by us, are the green original technology true to the name and will provide the best value. E&D Global promises to go with you as a global leading company for environment through commercialization of sludge disposal. Thank you.
- Main Product
Related Products

SUBMERSIBLE PUMP

15HP concrete floor grinding and polishing machine

High Pressure Spray Hose
,_Smartphone_dryer,_heating_mobile_2.jpg)
Mobile Dryer, Smartphone dryer, heating chamber(RG-202)

YN-COUPLINGS